#LookForTheRiver, Jersey Water Works Opening Plenary Speech
On December 13, 2019 LRWP collaborator and coLAB Arts co-producer and Director of Education John Keller delivered the opening plenary to the 2019 Jersey Water Works annual statewide summit at the Hyatt Regency Hotel in New Brunswick, NJ. John talked about the intersection of art, and our work in the watershed. He gave lots of examples of our collaborative effort these past 5 years. With thanks to John for allowing the LRWP to share his words.
Good Morning Everyone,
Uh, oh. I have to be that first person who annoyingly chastises you for being lack luster in your morning greeting. Think of it this way. It is Friday! You are coming to have a great time at this symposium, learn lots of stuff, have some good conversations, have la meal and still be out by 2:30! And as long as you don’t have a boss who is a party pooper it’s highly unlikely that any of us are going to go back to the office for just a few measly afternoon hours so that means found time! Maybe you’ll stop by your favorite independent coffee shop and have a nice afternoon latte in your favorite reusable cup. Then go over to the local day-spa maybe get a message or a nice facial (as long as it doesn’t have any microplastics in it), then meet up with some friends or family for a movie afterwards, but you will bring your own refillable BPA free water bottle because you are a little dehydrated from the latte, message, and facial and don’t want to pay $12 for a bottle of water at the theater. Then you will get out of the movie and think to yourself… wow that was a pretty good day.
So, let’s start this over.
Good morning everyone!
My name is John Keller and I have titled this presentation. 5 years of art in 9 minutes.
I am the director of education and outreach for a non-profit arts organization called coLAB Arts. You can find us on all the social media stuff as @colabarts.

I am here to tell you a story. The story is how an arts organization found itself motivated and inspired to facilitate conversations around our watersheds, and our relationship to water.
First, a little background. What is coLAB Arts and how does our mission drive us to collaborate with non-arts based social advocacy organizations, government institutions, and community groups?
Our mission is quite simply an equation. We engaged artists, advocates, and communities to created transformative new art-work. For us transformation must be three things. It must be sustainable, positive, and community focused. We work in areas as diverse as juvenile justice reform, transgender rights, domestic violence prevention, and dignity for our immigrant neighbors.
But this one is about water. So here we go.
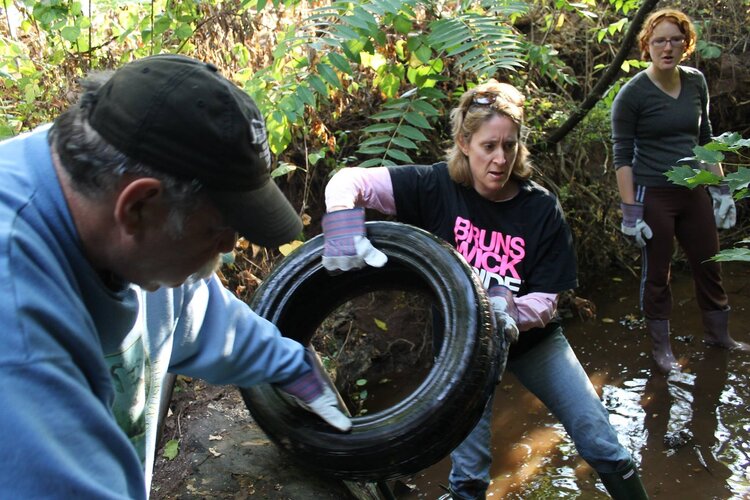

In 2015, myself and two coLAB Arts’ board members attended a watershed education workshop with the then recently formed Lower Raritan Watershed Partnership (LRWP). After the workshop we adopted a local stream and found what so many find in our urban areas: a stream in need of some love. We asked ourselves what we ask ourselves whenever engaging with a new advocacy concern:
How does the artist engage in this space?
What are the core issues that the advocacy partners are wrestling with? What are the historic contexts? What are the socio-political barriers to equity, diversity, inclusion, Justice and Access that the arts might help dismantle? Who are the communities not yet at the table? What are the questions not being asked? What are the ways artists can influence and augment research? – quantitative and qualitative data gathering. What are the complex ideas that artists can infuse into the conversation to make advocacy and even infrastructure better?

When LRWP heard these questions. And challenged us with some of their own for us to ponder. It was kismet. We began working together. Two organizations, arts and science. We formed a working group of artists, landscape architects, community organizers, and civic scientists, to wrestle with arts-based interventions to our natural and built environments. Early recognition from the American Architectural Foundation and their Sustainable Cities Design Academy gave us the opportunity generate bold ideas around on how the arts can drive sustainable changes to complex structural challenges.

We centered on a seemingly simple idea to drive the story of the work. It is the idea that the river is both a physical entity in our landscape, but it is also a powerful metaphor in our daily lives. It is all around us. It does not just exist in the physical limitations of the banks of a body of water, but it exists in our storm water systems, in the run-off from our homes, in our sprinklers, our faucets, in our dreams for quality of life, in our stories of migration, and our desperation in times of crisis. We began asking ourselves as well as the artists and communities brought into the work to #LookForTheRiver in all things.

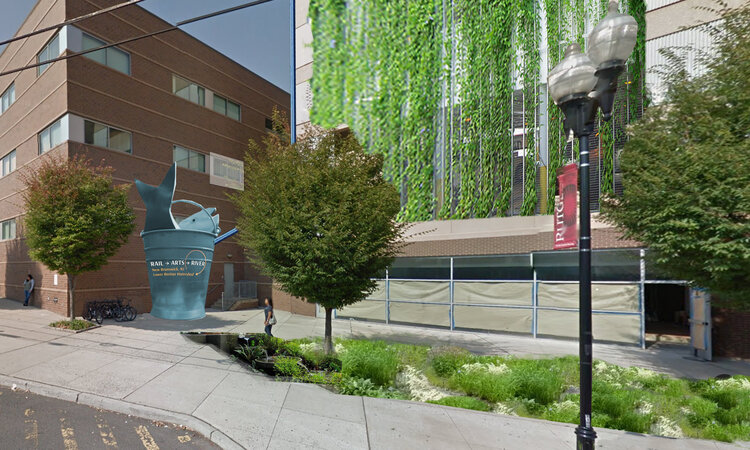
We began work in earnest. Going alongside the LRWP on stream clean ups. Participating in macro invertebrate trainings, touring spaces and landscapes that maybe weren’t the most obvious places of water stewardship. We began engaging professional artists through programs like our National Endowment for the Arts funded residencies where we partner an artist with a non-arts based organization and task each with creating an engaged arts project that facilitates a conversation with community that generates new works of art inspired by some big problem or question that advocacy org is wrestling with. The model of that residency which now has multiple artists with a diverse group of organizations is successful in no small part to LRWP piloting that program our first year. Our Watershed Helping Hands Sculpture Project on display in the lobby is one such example of one of the community based art engagement programs that resulted from that artist residency.
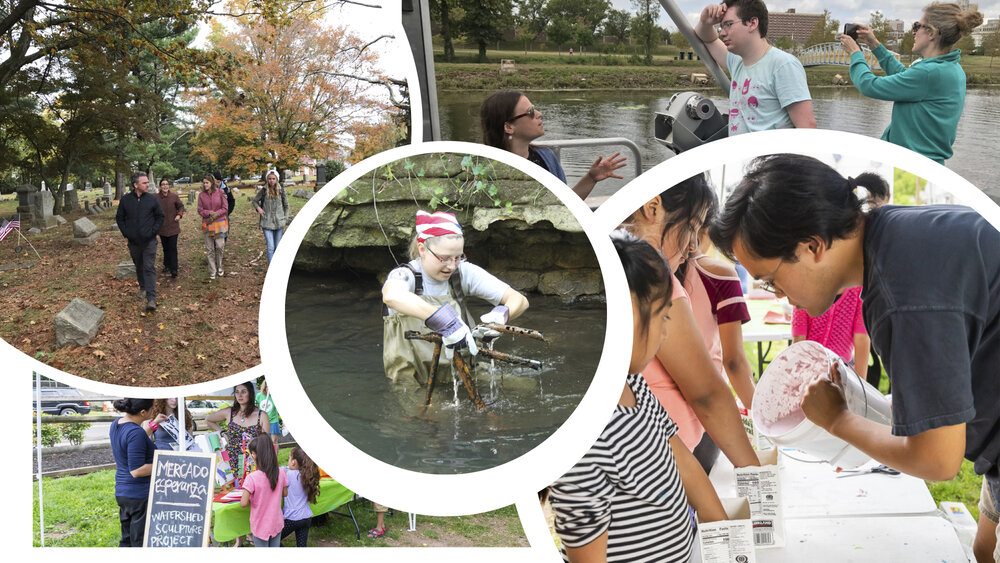

Once the communities have been engaged and you have built a critical mass of participation. You have to think next steps.
At the end of the day we are an arts organization and the greatest way to partner with artists is to provide opportunities for them to create bold artistic gestures.
Our work has been both conceptual and literal.
We have used the process of cleanups, data collection and public access as our points of inspiration to create works that both reuse found materials as well as engage with artists from diverse backgrounds and disciplines such as sculptural work, dance, theater, and mixed media.
To integrate both professional arts creation with community arts creation. Recognizing that while not everything can be called great art, great art can come from anywhere. We balance the ethereal of the performative with the substance of created artifacts; both a natural growth from a new communal education on watershed health and quality and the provocation of a call to action.
When this happens a new kind of reality might be possible. Where if we truly look for the river in all of the aspects of our lives. We begin to question why is it absent? And we see our spaces built in essence to do whatever they can to keep the river out. To blot it out from our landscape…
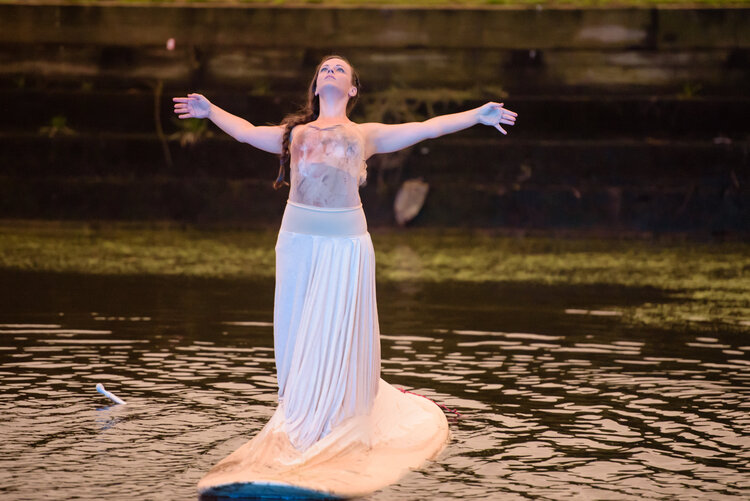
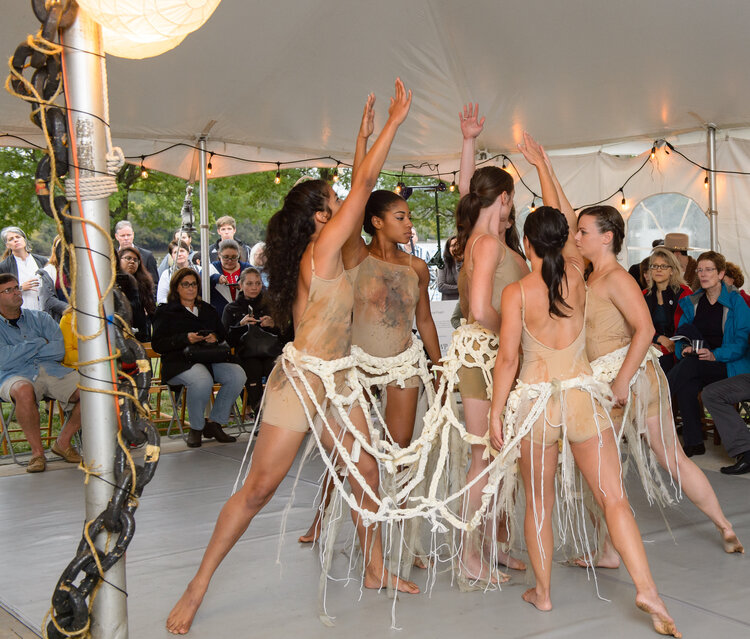



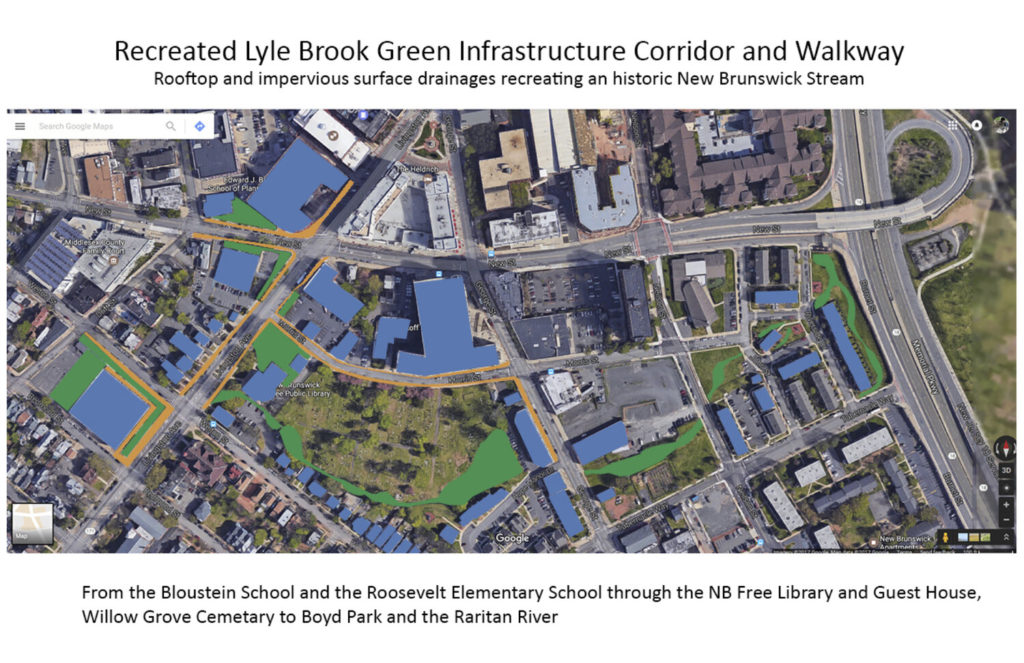
But when you create the potential for new vision we can inspire ourselves, our planners, and political leaders to reintegrate the river into our lives; into our built cities, and our story telling. Accepting the river back becomes our way of solving infrastructure problems. Like a new art and history based greenway connecting public spaces through the heart of an urban area, or an art and green infrastructure concept project which includes a two-story sculpture work that becomes a wayfinding landmark, urban beautification, and a five thousand gallon cistern to keep water run-off from reaching the storm water system in times of flooding.
When empowering communities to create art that allows them to connect with both their environmental and social justice history we can make space to dream about ways in which we can work with our built communities to remember the landscape of our past. And find new ways to interact with it.
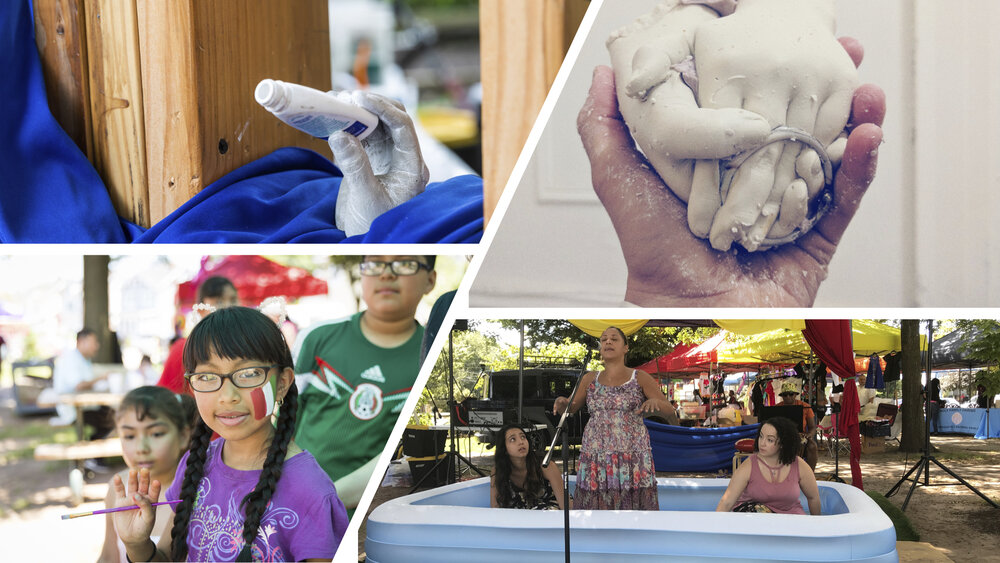


The arts are in incredible communicative tool. But the first act of social justice is to listen. Our creations cannot come before we first strive to listen with the intention of learning. Artists and water experts need to engage in this process together. When the artist is involved in the process – not just brought in at the end to slap some paint on a wall, not just asked to develop the PR or marketing strategy, rather allowing the artist to be in response to this listening process.

In 2019 we began an oral history archive which is about capturing those stories. Balancing the narratives. We research and collect the stories perhaps lost, perhaps suppressed, perhaps forgotten, around one very simple idea: Water is everywhere, and water is important to everyone. And then doing what we do… make are that is in response and helps us all frame a greener future.



