Article and photos by Joe Mish

Black oak leaves are ablaze in the most incredible orange color, which makes you wonder how the black oak got its name.
A robe of many colors is October’s alone to wear. It is a coarse cloth, woven with silken threads of yellow and orange, melting into the extreme end of the red spectrum. Set against a clear blue sky, the colors radiate with brilliance. While the sun is otherwise occupied behind gathering clouds, the colors are no less extraordinary, as they hold their sharp contrast, presenting with a soft matte finish.
As the robe is placed upon the earth’s shoulders, the colors slowly flow downward in an infinitely slow progression, best seen from high above the earth. With that image in mind, it is easy to visualize autumn as a living creature leaving a momentary trail of color across the breadth of the tilting earth.
An alternative to a live, time lapsed satellite image of autumn’s gradual crawl across the latitudes, is best seen from a lofty vantage point with expansive views. Though the view is static, the full range of colors is on display. The cloth of the colorful cloak lies tight against the contour of the wooded mountains, each undulating feature of the landscape accentuated by shade and light. On a typical sunlit October day, herds of white billowy clouds drift across the blue sky followed on the ground by their shadows trying to keep up. As the lagging shadows flow across the colorful mountainsides, the tints change for a brief moment to provide a sense of movement to an otherwise still image. The scene is more dramatic if you can imagine the passing shadows being that of the artist’s hand working as you watch.
Retreating from distant views to stand within the October woodlands, individual trees and stands of trees become the focus. Each species resplendent in their own genetically defined color, modified to some degree by soil conditions, specifically, available nutrients and moisture. Instead of looking at a mass of treetops where smudges of varied colors blend together, we now see the pixels that make up the distant image.
Comparing trees of the same species, we can see the individual variation of color. Many trees with yellow leaves such as hickories, Norway maples, cherry and tulip poplar trees are very consistent in color. Oaks, sweetgum and some maples, whose leaves have a red component, show the most diversity.
The most glorious displays of fall color are where we find them, scattered among the local landscape. Each, an emissary heralding the arrival of autumn; apart from the mass of color sweeping across the land.
We all have a perennial favorite we watch on a daily basis to gauge the progress of autumn color.
A lone white oak in the middle of a field or a native red maple pressing against the chain link fence in the backyard, as seen from the bathroom window, serve as daily alerts.
Among the many autumn images accumulated in my experience, the one that keeps appearing is an old abandoned farm road lined with Norway maples, all the same size. The tree tops form a tight canopy over the road, keeping it clear of weeds and paving it with a golden carpet of fallen leaves. The length of the yellow paved road has a hint of a vanishing point that beckons a traveler to follow deeper into the fire of autumn color.
Author Joe Mish has been running wild in New Jersey since childhood when he found ways to escape his mother’s watchful eyes. He continues to trek the swamps, rivers and thickets seeking to share, with the residents and visitors, all of the state’s natural beauty hidden within full view. To read more of his writing and view more of his gorgeous photographs visit Winter Bear Rising, his wordpress blog. Joe’s series “Nature on the Raritan, Hidden in Plain View” runs monthly as part of the LRWP “Voices of the Watershed” series. Writing and photos used with permission from the author.
Article and drawing by Maya Fenyk, age 13
Hello! I am Lynx Rufus, but you can call me Blossom the Bobcat. I am New Jersey’s only native wildcat, and have been on New Jersey’s endangered species list since 1991. Sightings of me in the Lower Raritan Watershed and throughout the state are increasing, but are still rare.
You might think “Oh, bobcats must survive just fine. They are at the top of the food chain. They have no predators.” I am sorry to say, that’s just not true. Some of my predators are mountain lions, coyotes, foxes, owls, wolves and humans. I can’t say I blame them as I also prefer a carnivorous diet. My prey includes rabbits, rats, squirrels, ground-nesting birds, turkeys and even small or sick deer. But predator threats are not my biggest concern.
My species used to be abundant and flourishing in the coniferous and mixed forests of New Jersey until humans started deforesting our homes. Clearing land for retail, corporate and housing developments has a huge impact on my survival. And disruption of our habitat by pipelines has huge impacts on us and other endangered, threatened and special concern species. Other issues that affect me are hunting and being hit by cars. Getting hit by cars, development and pipeline installation are linked. Fragmentation of my habitat makes it hard for me to find shelter from the weather, cover for hunting and raising my babies, and forces me and my family to cross roads to find our dinner and safe spaces to hide. Please slow down through forested areas! When humans ruin my home, push me onto their roads, and drive too fast through the woods it really gets my angry purring going.
The New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection’s Endangered and Nongame Species Program’s Bobcat Recovery and The Nature Conservancy’s Bobcat Alley are both doing a great job restoring bobcats in New Jersey, but plans for pipelines and proposals to reduce protections under the state’s Freshwater Wetlands Protection Act and the federal Clean Water Act put our population recovery into question.
I must head to my den to check on my kittens, but I want to let you humans know how important it is to keep track of the numbers of my species. To report a bobcat or other endangered species sighting, please contact NJDEP. Thanks! And I say that with a final meow!

Article and Photos by Joe Sapia
Note: The yard references are to my house in the section of Monroe between Helmetta and Jamesburg in South Middlesex County. My yard is in a Pine Barrens outlier on the Inner Coastal Plain, the soil is loamy, and my neighborhood is on the boundary of Gardening Zones 6b (cooler) and 7a (warmer). Afield references are to the Pine Barrens around Helmetta, unless otherwise noted. Photographs are for the period covered, unless otherwise noted.

The Van Dyke Farm at Pigeon Swamp, South Brunswick/Middlesex County, where growing crops meets the woods.
VAN DYKE FARM: A favorite place to shoot photographs of mine is the Van Dyke Farm at Pigeon Swamp in South Brunswick/Middlesex County. It offers big-sky views to the west and the setting sun. See http://www.middlesexcountynj.gov/About/ParksRecreation/Pages/PR/VanDyke.aspx.
SOURLAND MOUNTAIN: I hiked one of my favorite Midlands places, Sourland Mountain on the boundary of Somerset, Hunterdon, and Mercer counties with a club I have been a member of for about 35 years, the Outdoor Club of South Jersey. On the mountain, I saw various flowers in bloom: showy orchid, “Galearis spectabilis,”; rue anemone, “Anemonella thalictroides”; and spring beauties, “”Claytonia virginica.” Being on the Piedmont with its rocky terrain, Sourland Mountain is much different than my generally flat and sandy Pine Barrens around Helmetta.

The Roaring Rocks boulder field on Sourland Mountain. Notice the hikers in the upper part of the photo.

A showy orchid on Sourland Mountain
FLATLANDERS VERSUS HILLTOPPERS: For purposes of this writing, New Jersey has four geological areas, which run northeast to southwest: from west to east, Ridges and Valleys, Highlands, Piedmont, and Coastal Plain. (The Coastal Plain can be divided into two areas, Inner and Outer, making it five regions.) Generally, the Midlands are divided into the Piedmont and Coastal Plain, with distinct characteristics. The generally flat Coastal Plain has white, sandy soil (think Shore and Pine Barrens) and dark soil (think conventional farming areas). The rolling Piedmont has red shale and traprock boulders.

Piedmont red shale at Sourland Mountain, which is in the background.

Traprock boulders on Sourland Mountain.

Coastal Plain dark soil at Cranbury/Middlesex County.

White, sandy soil in the Pine Barrens of Helmetta on the Coastal Plain.
FULL MOON AND PLANTING: The full moon was May 10, Wednesday, and some feel it is OK, now, to plant warm weather crops. Not me, especially with the cooler weather we have been having. I am still waiting for May 20 (if it warms up) to June 1 (if it remains on the cool side). Then, I will plant my warmer season crop – tomatoes, mushmellon, sweet corn, and cucumbers, along with zinnias to attract pollinators and for their beauty.

The near-Full Corn-Planting Moon. The full moon was Wednesday, May 10.
FOOD GARDEN: I weeded for the first time around the cool weather crops — “Salad Bowl” heirloom lettuce, “Rainbow Blend” carrots, and “Sugar Daddy” snap peas, all “Lake Valley Seed Company” brand — that have sprouted. I continue watering the garden.

Lake Valley Seed Company “Salad Bowl” heirloom lettuce growing in my garden.
WATERING THE FOOD GARDEN: My goal is to give the food garden a thorough watering by 10 a.m. This allows the garden to retain water, rather than have the water evaporate in the heat of day, and allows the garden to dry by the dewy nightfall to prevent fungal growth.
KEEPING WILDLIFE AWAY, CAYENNE PEPPER: I was talking a waitress at the Dayton Diner in South Brunswick/Middlesex County. An experienced gardener, she recommended using cayenne pepper as a method of pest control around the garden. I plan on trying that.
ALONG THE SOUTH RIVER: My travels took me across the South River at Old Bridge village on the boundary of Old Bridge, Sayreville, and East Brunswick, all in Middlesex County. On my way back, I stopped to shoot photographs between Old Bridge village and the New Causeway on the boundary of South River and Sayreville, both in Middlesex County. The South River is formed by the meeting of Manalapan and Matchaponix brooks on the Spotswood-Old Bridge boundary at DuHerNaL Lake/Middlesex County. (DuHerNaL Lake gets its name from the three companies that had used it as a reservoir: DuPont, Hercules, and National Lead.) Normally, I do not think of inland self, 25 or so miles from the Atlantic Ocean, living near salt water, but the tidal effect begins at the bottom of the DuHerNal Lake dam, only a little more than 4 miles from my house.

The South River at low tide at Old Bridge village.

The South River at low tide at the New Causeway on the South River-Sayreville boundary. This scene looks upstream toward the railroad bridge and the South River Boat Club — Sayreville on the left, South River on the right.
KILLDEER: When I was at the South River at Cannon Brothers Park in South River, I spooked a killdeer, “Charadrius vociferous.” The species screeches a “kill-deer” call. Because of the way the bird was acting, panicked but not leaving the area, I suspect it had a nest nearby it was trying to divert me from. An adult killdeer will even fake a broken wing to get a predator to follow it, rather than have the predator attack the ground nest. I could not find a nest.

A killdeer along the South River in South River.
TURKEYS: Some thoughts from Bob Eriksen, the retired state turkey biologist, on “Meleagris gallopavo,” “…Wild turkeys that have adapted to suburbia will sometimes nest in among shrubs in a yard. I had one nest next to a gravestone in a cemetery. Most of the time turkey nests are in the woods or in an overgrown field. Hens will tuck in next to a tree trunk, at the base of a shrub, or in a blowdown, especially if there is a branch within a few feet. They like to have a bit of overhead cover. Once the grass in hayfields is tall enough to hide the hen crouched down (usually second week of May), a hen turkey will nest in a hayfield. Cover is the main consideration. Hens are pretty secretive approaching the nest. They may circle or use different approaches when they go to the nest to lay. When the clutch is large enough (10-12 eggs), she will begin to incubate. For the first couple of nights after she has completed her clutch, she may tree roost, but that changes fast. Once incubation begins, the hen will be on the nest 20 or more hours a day.” (A shout out to Bob for always being so helpful.)
JERSEY MIDLANDS LORE: Another good source of information is legendary Helmetta outdoorsman Ralph “Rusty” Richards, 84-years-old. During one of our occasional breakfasts of members of 100-year Helmetta families, Rusty was talking about deer-hunting. In the early part of the 20th Century, white-tailed deer, “Odocoileus virginianus,” were almost gone from New Jersey because of over-hunting. As the state brought them back, they gradually re-settled. About 1950, they were in the Broadway Woods area of South Brunswick/Middlesex County, only a few miles from Helmetta, according to Rusty. Then, about 1955, they were settled around Helmetta, Rusty said.

In 2011, Rusty Richards with “opienki” mushrooms, genus “Armillaria,” in the Pine Barrens around Helmetta.
BOBWHITE: Did I hear a bobwhite quail, “Colinus virginianus,” calling in my neighborhood? If so, it would have been a return to my childhood when one could hear the “Bob White” call at night. Bobwhites have become rare in New Jersey because of habitat loss, but, in recent years, there has been an effort to welcome them back. So, was it a wild bobwhite or not? I do not know….
TICKS: Reports are still coming in on how bad a tick season it is.
I am hearing reports of deer ticks, “Ixodes scapularis,” and lone star ticks, “Amblyomma americanum.” Various reasons may be causing the problem, including warm weather generating acorn growth and, in turn, the acorns providing abundant food to tick-carrying animals, along with the recent rainy weather. “More rain typically enhances tick season,” said meteorologist Steve DiMartino.
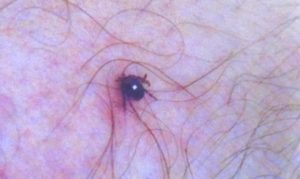
A lone star tick on my leg. Lone star ticks are easily identifiable by the yellow dot on their backs.
PINE BARRENS AROUND HELMETTA: Pink lady-slipper orchids, “Cypripedium acaule,” continue to bloom. I know of a spot that has about 75 lady-slippers, with about five in bloom. If you see a pink lady-slipper, look around for more in the area; I see them in clusters. And do not pick them!

A blooming pink lady-slipper orchid, with another, left and to the rear of the blooming orchid, poking through the ground.
SUNRISE/SUNSET: For the week of May 14, Sunday, to May 20, Saturday, the sun will rise at about 5:40 a.m. and set at about 8:10 p.m.
WEATHER: Go to the National Weather Service forecasting station for the area, http://www.weather.gov/phi/.
THE END-OF-THE-WEEK RAIN: I look to a thorough rain around May 15 to green up the woods for the season. The steady, heavy rain of Saturday, May 13, should have accomplished that. By late Saturday night as the rain continued, my rain gauge showed 2.3 inches.
WEATHER: Go to the National Weather Service forecasting station for the area, http://www.weather.gov/phi/.

A red-bellied woodpecker, “Melanerpes carolinus,” sitting in a pitch pine, “Pinus rigida,” in my backyard.
Joe Sapia, 60, is a lifelong Monroe resident. He is a Pine Barrens naturalist and an organic vegetable-fruit gardener.
He gardens the same backyard plot as did his Italian-American father, Joe Sr., and his Polish-immigrant, maternal grandmother, Annie Poznanski Onda. Both are inspirations for his food gardening. Joe is active with the Rutgers University Master Gardeners/Middlesex County program. He draws inspiration on the Pine Barrens around Helmetta from his mother, Sophie Onda Sapia, who lived her whole life in these Pines, and his Grandma Annie.
Article and photos by Joe Mish

Doe and fawn kick up thie heels in the cool water of the South Branch of the Raritan.
Deer love to wade in the river, even at noon, on the hottest summer days
High Summer Drama
The low dam at Red Rock Lake turned the water of the South Branch inside out to create an unbroken white line along its length. Here, the living water falls upon itself in an act of resuscitation, no different from lifesaving CPR.
Below the dam, the freshly oxygenated water rushes to fill a deep cut in the river bed funneling its energy, impeded elsewhere by shallows and exposed tree roots.
At the start of each trip, below the lake, I do an upstream ferry across the fast water as a tribute to the river’s energy. I provide the proper angle and the river obliges with a free ride across the current with no downstream slip. Angle the bow into the opposing current and the boat spins into a downstream posture to start another river journey through the high summer season.
The water’s surface reflected the bright blue summer sky and lush greenery along the shoreline. The river banks falsely declaring a limit to the infinite reach of the sky.
August is indeed high summer, all plant life at full maturity vying for sunlight, slender and long, eager to dance in the gentle summer breeze.
Lush, light green grass hung over the river bank in one treeless stretch when I saw a painted water snake swimming to the opposite shore. Only the head of the snake, which created a small wake, betrayed its presence. As I neared, the snake slightly altered course. A few feet from the left shore it suddenly rose up, as if struggling. It would have had to press up against something to rise as high as it did and since the water was still quite deep, it begged investigation.
In an instant a snapping turtle’s head broke the surface of the water, draped in dark green grass and holding the snake near the end of its tail end. Such a non vital hold promised a long struggle and struggle the snake did. I began to record images of this fight for life, so inconsistent in such a peaceful setting.

The surprise reptilian clash held the colorful snake in close contrast to the turtle’s head. The turtle’s mouth was more of a razor edged compact beak, a creamy tan with fine vertical black lines. The round orb of its bulging eye and dark pupil were the only recognizable shapes against a pattern of dull and dark brown irregular patches that covered the turtle’s head. The black pupil was surrounded by three thick, dark brown streaks radiating out at 3, 6 and 9 o’clock positions, a pattern quite like a style of crosshair seen in some rifle scopes.

The painted water snake, alias, northern water snake, by its nature, was a linear billboard showcasing a recurring pattern of a variety of shades of tan and orange, and black, the pattern getting tighter and more compact near the tail. The snake must a have just shed, as its colors gleamed to a high shine, enhanced by the water.

This is a painted/northern watersnake; the colors are more brilliant just after it sheds its skin.
This snake recently dined on some other good sized aquatic critter, now seen as the large bulge in the snake’s stomach.
The fight raged on for several minutes, coming to an abrupt end when my boat drifted closer to the combatants. The turtle became intimidated and released the snake, drama over, no evidence of what had just taken place except for some digital images. I imagine the education of both animals was advanced by their encounter.
A mile down river the scenery changed as the main current, hugging the up heaved, high, red shale cliff, was slowed by a gravelly shoal stretching across the river. Here, the high cliff disappeared back into the ground to give way to a woodsy landscape. The river narrowed and water became deeper. The tree tops reached across the river to give the impression of a leafy tunnel. This was a straight, short stretch that now opened up to allow the first river view of the Sourland Mountains. An island divided the river here, diverting more water to the right passage around a sharp bend, than to the left.
The island had a few small trees smothered in tall sun drenched, light colored grass that reached into the shallow water. Recent events had kept the water level far below normal and as a result, the delicate grass began to grow and prosper where it normally would not. The water level on this day was now raised and flooded the fine green grass.
Here, the river bed follows a deep, narrow cut, close to the right shore and obstructed with fallen trees. From the island to the cut, the river was impassably shallow. Coming around sharp bends on an intimate river usually holds the best surprises. Today was not a disappointment as a doe was standing in the water staring at me from 20 feet away.
There was little I could do keep still, as the narrow passage along the bank required some quick paddle strokes to avoid being grounded. That mandatory movement caused the doe to run off, seeming more annoyed than frightened. Behind her were two spotted fawns that splashed away through the shallow water and tender grass. The one fawn ran toward a second doe, keeping close to her heels. Alerted, the doe and fawn ran a few paces and stopped. They really were reluctant to end their mid day romp in the cool river. Water droplets flew in slow motion as the doe and fawn ran off two more times. The light green grass was finely detailed, while the same green scene reflected in the water, lost the detail, but kept the essence of the verdant color to make the foreground and background indistinguishable from each other. The two deer, resplendent in their red summer coats, the fawn, speckled white, complimented the green background.

The water exploded from splashing hooves to energize the scene, as it stood in contrast to the reflective water. Raising her pure white tail, the doe provide an exclamation mark to the perfect image to represent high summer on the South Branch.
Author Joe Mish has been running wild in New Jersey since childhood when he found ways to escape his mother’s watchful eyes. He continues to trek the swamps, rivers and thickets seeking to share, with the residents and visitors, all of the state’s natural beauty hidden within full view. To read more of his writing and view more of his gorgeous photographs visit Winter Bear Rising, his wordpress blog. Joe’s series “Nature on the Raritan, Hidden in Plain View” runs monthly as part of the LRWP “Voices of the Watershed” series. Writing and photos used with permission from the author.
Article and photos by Joe Mish

This female red phase screech owl with erect ear tufts and large eyes looks as ferocious as it sometimes sounds.
The calm starlit night, made blacker by the dark phase of the moon, was the perfect setting for a peaceful night’s sleep. The windows were wide open and the air scented with honeysuckle as the gentle sounds of the night played a sleepy time lullaby.
Deep sleep and dreams were well under way when a primal scream, just outside the window, vibrated the walls. Everyone sat up, hearts beating wildly, sleeping coonhounds unleashing unheard of sounds that must have been reserved in the event they ever treed the devil.
Before my heart beat slowed, I figured the sounds had to come from a screech owl perched on a tree limb six feet from the bedroom window. The unearthly screams were one selection of screech owl vocalizations that include rapid clicking of its beak and a gentle wavering call that, through association with spooky movies can easily raise the hairs on the back of your neck.
The volume of a screech owls’ motivated scream is inconsistent with its small size. The eastern screech owl is about 9 inches tall, weighs around 6 ounces with a 24 inch wingspan and easily fits through a three inch nest box hole.

Adult red phase screech owl perches in 3″ hole of its nest box, note the feet gripping the edge of the opening.
Eastern screech owls come in two colors, a red phase and a gray phase. Its physical appearance, while perched, gives the impression it is missing the lower half of its body. During the day with its eyes shut it blends in so perfectly with its background it is difficult to tell what part is what. The owl seems to suddenly appear from the background when it opens its large yellow eyes.

Eyes closed, these owls seems to disappear with no reference to top or bottom or recognizable form.

Screech owls seem to comfortably tolerate humans and can be seen, and will nest, in proximity to homes and buildings if a nest box is provided.
Late June early July, a screech owl would show up whenever I went into the backyard around dusk. It would follow me around and click its beak from a nearby branch. I have no idea what motivated that behavior but that owl provide plenty of photo opportunities.

Then there were the memorable Christmas day visits. One Christmas morning I went to the open woodshed to replenish the woodstove with an armful of oak. There, staring me in the face from four feet away was a gray phase screech owl. It stayed put while I gathered the wood but was gone when I returned with my camera.
A few years later on Christmas night, a red phase screech owl perched a few feet off the ground in a weeping cherry tree. The little owl was spotted by the car’s headlights. It remained undisturbed while I did capture its image.

A late Christmas present in full feather, delivered at the front door.
Screech owls may just as well be found in deep woods. I have a great image of a red phase owl sitting in a healed hole in the side of a large tree trunk about eight feet off the ground. Other sightings have been in places where mature sycamore trees grow. Often, broken branches will leave a cavity that overtime becomes deeper, forming a perfect nest or day time resting place for this diminutive owl.

Though screech owls are quite common, you may never see one. Think of them as a night time radio host whose show you listen to all the time but never put a face to the voice. Hear a sampling of screech owl calls at: https://www.allaboutbirds.org/guide/Eastern_Screech-Owl/sounds
Author Joe Mish has been running wild in New Jersey since childhood when he found ways to escape his mother’s watchful eyes. He continues to trek the swamps, rivers and thickets seeking to share, with the residents and visitors, all of the state’s natural beauty hidden within full view. To read more of his writing and view more of his gorgeous photographs visit Winter Bear Rising, his wordpress blog. Joe’s series “Nature on the Raritan, Hidden in Plain View” runs monthly as part of the LRWP “Voices of the Watershed” series. Writing and photos used with permission from the author.
Article and photos by Joe Mish

The osprey from Maine searches the clear water of the South Branch for a meal as she takes a break from her 2,500 mile journey north. The letters, DV, can be seen on the blue band attached to her right leg.
The warmth from the mid-morning sun felt good on my back as I paddled the low, clear water of the South Branch. The cloudless sky, directly above, was a darker shade of blue, its intensity pure and endless, and mesmerizing. It compelled me, as the devil’s advocate, to search for just a single speck to interrupt its perfection.
Suddenly a shadow sped across the water, momentarily stealing the sunlight. I instinctively looked up to catch a glimpse of an osprey circling above. The white head, streaked with a dark brown stripe, was instantly recognizable. The osprey proceeded downriver by making tight overlapping circles in its search for fish. It isn’t too hard to imagine some of these super intelligent predators realize a canoe is herding the fish ahead of it. When the osprey was about 150 yards downstream it tucked its wings and dove into foot deep water to come up with a large white sucker held fast in its black talons. The bird oriented the position of the fish to cut wind resistance as it flew out of sight.
Ospreys are ever present on the South Branch, typically from early spring to mid autumn. They feed primarily on live fish. I see them most often eating white suckers, a fish large enough to compensate for the energy spent to catch it.

Osprey on a riverside perch, dining on fresh fish during the 2014 NJ opening day of trout season.
Earlier this April, I noticed an osprey perched in the same location day after day. This wasn’t typical of the local ospreys that ranged far and wide in their constant search for food. I was able to get a few photos and noticed a blue band on the right leg and a silver band on the left. I reported the band to the USGS website, BandReports@usgs.gov, to find this osprey was banded in Portland, Maine, July 27th, 2011 while it was still in the nest, too young to fly.
Osprey migrate from the northeast, where they breed, to central and South America each fall, a trip of more than 2,500 miles. This bird was apparently on its way back to Maine and stopped to rest. Osprey, like other migratory birds, are very loyal to nest sites and return to the same location with great predictability.
Consider our visiting osprey will be 5 years old this July, and has 25,000 plus, frequent flyer miles on its account, you have to recoil in amazement, wonder and respect for its strength and tenacity. As osprey can live 25 to 30 years or more, the mileage really adds up.
Our Maine visitor, a female, as evidenced by her speckled décolletage, has a bright and long future and hopefully will stop along the South Branch again on her journey to and from Central America. No doubt other osprey are flying to northern breeding grounds through NJ, so the opportunity to spot a banded bird along the North and South Branch are quite good.
The reporting of banded birds is critical to wildlife research as it helps to unravel the mystery of migration, the location of breeding grounds, longevity, and other variables that impact the health and status of local and overall wildlife populations.
New Jersey is now using red bands for osprey and from Ben Wurst at conservewildlifenj.org, as per USGS; “Green anodized bands are being used in NY. Purple anodized bands in MD and VA. Red anodized bands (like ours, but with alpha code A&B 00-99) in PA (permit is expired now). Blue anodized bands in MA, ME & Ontario.”
The preponderance of osprey nests in NJ are along the Delaware River and Atlantic shoreline, its estuaries, bays and rivers, so keep an eye out for banded birds and report them to BandReports@usgs.gov . The researchers are as excited about a band report as you and will send a certificate of appreciation with relevant data about your bird. Many species of birds are banded, so don’t forget our eagles, hawks and songbirds. Opportunities abound as NJ is on a major flyway, the rivers being main exit and entrance ramps to our backyard.

*Joe sent us an update to this post, a photo of the exact location in Maine where the osprey was born. Photo courtesy of Lauren Gilpatrick at the Biodiversity Research Institute, Portland Maine.
See, http://www.conservewildlifenj.org/education/ospreycam/ for more details about NJ osprey project and live osprey cam.
Special thanks to Robert Somes, Kathy Clark and Ben Wurst for their enthusiastic help and support.
Robert Somes, Senior Zoologist
NJ Division of Fish and Wildlife
Endangered and Nongame Species Program
Kathy Clark,CWB,
NJ Division of Fish and Wildlife
Endangered and Nongame Species Program,
Ben Wurst, Habitat Program Manager
New Jersey Osprey Project
Author Joe Mish has been running wild in New Jersey since childhood when he found ways to escape his mother’s watchful eyes. He continues to trek the swamps, rivers and thickets seeking to share, with the residents and visitors, all of the state’s natural beauty hidden within full view. To read more of his writing and view more of his gorgeous photographs visit Winter Bear Rising, his wordpress blog. Joe’s series “Nature on the Raritan, Hidden in Plain View” runs monthly as part of the LRWP “Voices of the Watershed” series. Writing and photos used with permission from the author.
Articles and Photos by Joe Mish

A cooper’s hawk flies off after landing in a holly tree where it jumped from branch to branch in an effort to flush a hiding songbird into the open.
Midwinter is a great time to catch a glimpse of local wildlife, especially hawks, as these large birds stand in dramatic contrast to the gray-brown leafless trees in which they perch.
The most common hawk in our region is the red-tailed hawk. Comparatively large, the adults are recognized by the bright russet colored tail. This is the only hawk whose tail is not banded or bordered by a contrasting color. The young birds have barred tail feathers, alternating russet and white, with no distinct borders.

Easy to spot at highway speeds, the light breast and faded red tail stand out like a beacon when perched in trees along the roadway. Locally, I often see these hawks atop telephone poles near pastures and flood plains where they scan the open area for small mammals and ducks. Some red tails specialize in killing gray squirrels, a worthy meal for such a large bird whose energy expenditure in the winter would hardly be covered with mice or voles.
During a winter freeze when most of the river is solid ice, there are always open sections where ducks concentrate in the water and on the ice. A red tail will make an easy meal, especially of the smaller wood duck, flushing it into the air or catching it as it naps on the ice.
Last winter I watched an eagle feeding on a wood duck, speculation was the eagle took the duck from a red tail as eagles are notorious for stealing game from ospreys and hawks.

Muskrats are also high on the midwinter menu as the males often travel during the day over ice and snow as they seek food and females to breed.
A hawk requires a large nest and now is the time to scan the treetops and high tension towers for these stick built structures. One local hawk has adapted to a giant oak in someone’s backyard bordering a cluster of recently constructed homes. I have seen several local nests situated high in sycamore trees along the river. Hawk nests are relatively flat and large, not to be confused with squirrel nests which are numerous and quite round, generally built at a lower level, among thinner branches. Red tails will also use ledges as a base for their nests.

The ultimate adaptation belongs to the red tail known as, Pale Male, whose life is well documented in film, media and print as he has mated and bred several generations of hawks among the skyscrapers in mid Manhattan. His age is estimated at 24 years. Here is one site dedicated to Pale Male.
Marsh hawks share the sky with red tails and characteristically conduct ground hugging flights across overgrown fields, flood plains and grasslands and have an ability to hover in place. These hawks are slightly smaller than a red tail with dark brown coloration and a boldly banded tail. The key to identifying a marsh hawk is the bright white rump patch. These hawks are common, though not often seen and are known to migrate while red tails remain as full time residents.

Aside from red tails, the most often seen hawks are the coopers and sharp-shinned hawks. The coopers being slightly larger than the sharp shinned. Both hawks feed on songbirds and small rodents. As each is similarly marked, identification is always controversial. More often than not, someone will submit a photo of a hawk to a website asking if it is a coopers or sharp-shinned and the replies are often split, each summarizing why they made their choice. I see the larger coopers preferring doves and rabbits while the sharp shinned has left piles of bluebird, indigo bunting and flicker feathers about the yard.
Lastly, look for the diminutive sparrow hawk, now known as the kestrel, typically perched on telephone poles and wires along open fields. This bird is about the size of a large dove, feeds on insects and small rodents. Kestrels are known for hovering before they dive on their prey and this stationary flight is a good identifying characteristic. The males are brilliantly marked with blue, shades of russet, black and white. At first glance a perched kestrel will appear as a songbird so be sure to give a second look. They are considered threatened in New Jersey and a nest box program and monitoring effort is having a positive effect on their recovery. The birds are easily baited and trapped for tagging and data collection.

This is the winter of the hawk and hardly a commute is possible without being evaluated by a feathered predator. They can see you, can you see them?
Author Joe Mish has been running wild in New Jersey since childhood when he found ways to escape his mother’s watchful eyes. He continues to trek the swamps, rivers and thickets seeking to share, with the residents and visitors, all of the state’s natural beauty hidden within full view. To read more of his writing and view more of his gorgeous photographs visit Winter Bear Rising, his wordpress blog. Writing and photos used with permission from the author.
by Joe Sapia
As the 1800s turned into the 1900s, wild turkeys apparently were extinct in New Jersey.
“It’s a native species,” said Tony McBride, the state’s turkey biologist at the Division of Fish and Wildlife. “It requires large areas of upland forest interspersed with openings.”
Turkeys roost in trees, but it is important for the young to feed on insects, available in open areas, to get necessary protein.
But, at the turn of the 19th Century into the 20th Century in New Jersey, land was being cleared for farmland, resulting in the loss of forest habitat. Additionally, there were no limits on hunting turkey. Translated, turkeys disappeared in New Jersey.
“They were gone, as far as we know,” McBride said.
Today, though, the Pine Barrens Around Helmetta – as well as the rest of New Jersey, with an estimated population of 20,000 to 30,000 — are thriving with turkey. And they are easily seen – I see them often as I drive my Jeep down paved roads, for example.
Or I may get a glimpse of them in the woods, even though they are stealth and, when threatened by my approach, make sleek getaways – sometime simply scrambling into heavy understory and fitting in, camouflaged.
“They’re very wary,” McBride said. “They have good vision, hearing, and they taste good, so everything’s after them. They’re constantly on the lookout for predators.”
Turkeys can fly 55 miles per hour, once they get going.
“Turkeys are good fliers,” McBride said.
In January, I was attending an afternoon wake at a funeral home that backs up to the woods. On the funeral home grounds is open space. The funeral director mentioned how turkeys frequent the property. None were in sight when he said it, but, within minutes, there they were.
Even if one does not see them, their three-prong tracks are obvious on the ground or in snow.
“When we release birds in an area, they disperse,” said McBride, adding “every once in awhile,” turkeys, with a range of up to 2 square miles, will settle miles from the release point.
Bob Eriksen, the state turkey biologist from 1977 to 2001, said he once had a release in the Walpack area of Sussex County ending up in Sullivan County, New York, or 28 miles away.
The Pine Barrens around Helmetta have nice turkey habitat of woods and open space. Here, there is forest with farmland abutting it and utility right-of-ways cutting through it. Basically, that explains the re-population of turkeys here, apparently beginning in the late 1990s.
Looking back to the 1950s and 1960s, East Coast game farms would release turkeys. These farm-raised birds, however, “would persist (perhaps for a few years) and fizzle out,” not having the instinct for general survival and feeding, McBride said.
In the early 1970s, scientists learned restoration would be successful with releasing a “true wild stock” of adult birds, McBride said.
“There’s something to be said about these birds growing up in the wilds and passing the skills along,” McBride said.
Around 1977, 22 adult turkeys – 15 hens and seven toms – from New York and Vermont were released in Sussex County. Thus began successful restoration in New Jersey.
By 1979, New Jersey was moving around in-state birds, Eriksen said.
“When a turkey population is first established, the growth is really fast,” McBride said. “The thinking is the predators are naïve.”
Predators of eggs in the ground nests include skunk, raccoon, and crow. Predators of adults and babies include coyote, fox, red-tailed hawk, and great-horned owl.
Within four years of that 1977 release, it had been so successful “we were hunting them,” McBride said.
The Pine Barrens around Helmetta are part of Turkey Area 12, which runs north to south from the Raritan River to Interstate 195 and west to east from Trenton to the Atlantic Ocean from Sandy Hook to Belmar.
In 1995, the state opened a turkey-hunting season in Area 12, because the birds were well-established in the Sourland Mountain area to the west and the Colts Neck area to the east.
In 1996 and 1997, looking to populate the area between Sourland Mountain and Colts Neck, the state released 18 birds on Dey Road, Cranbury – eight birds over two days in January 1996 and 10 birds on Feb. 9, 1997.
A file card from Jan. 3, 1996, shows an adult female, caught in Hampton, Sussex County, and weighing 10-1/2 pounds, was released on the Simonson Farm on Dey Road in Cranbury.
Apparently these were the only two releases near the Pine Barrens around Helmetta, which are about 5 miles away. But that was all that was needed. Soon, turkeys were being recorded in those Pines.
My field notes indicate I first noticed turkey in the Pine Barrens around Helmetta in the fall of 1998.
November 28, 1999: “Turkey in tree in area behind Helen Maslanka’s house,” which is at Jamesburg Park.
January 20, 2001: “Tracks in snow by Jamesburg Dump/Manalapan Brook floodplain area.”
May 22, 2006: “Turkey, saw 2 on Washington Avenue” at Jamesburg Park.
May 25, 2008: “Saw turkey tracks in wet area” along Lincoln Boulevard.
March 24, 2010: “Saw a few wild turkeys on the other side of (Cedar) Brook, or behind the houses,” in Spotswood.
Early May, 2010: “Turkey trots up (Swing) Hill.”
April 14, 2011: “About 6:10 p.m. at the corner of Helmetta Boulevard and Old Stage Road, a turkey flew across Helmetta Boulevard from north to south.”
January 25, 2012: “A flock of turkeys in (Cranberry) Bog. Only heard them because they moved, rustled vegetation. Guess I spooked them.”
I have seen either turkey or its tracks in various places in the Pine Barrens around Helmetta: Snuffy Hollow, the Power Lines at the Cranbury Road farmland, behind Holy Cross Cemetery, in my neighborhood between Helmetta and Jamesburg, across Manalapan Brook from my neighborhood. Basically, they are all around.
Area 12 hunting records suggest the success:
In 1995, during that first season in Area 12, the area had 43 kills of the state’s 1,581. In and around the Pine Barrens around Helmetta, the kills were 3 in South Brunswick, 1 in Monroe, and 1 in East Brunswick, with no kills recorded in Helmetta, Spotswood, Jamesburg, and Old Bridge.
In 2012, Area 12 had 113 of the state’s 2,956 kills. In and around the Pine Barrens around Helmetta, the kills were 16 in Monroe, 7 in Old Bridge, 2 in Helmetta, and 1 in East Brunswick.
In Area 12, turkey hunting is allowed with shotgun or bow and arrow from late April to early May. (The state also has a fall turkey season, beginning in late October and running for one week, but that season is not open in Area 12.)
Turkeys mate from March into April. Nests are hidden on the ground, either in a field at the edge of a forest or amid shrubs or fallen tree in a forest.
“When they make their nest, you generally can’t see them,” McBride said.
A hen will lay about a dozen eggs during the last two weeks of April. About May 1, she will begin sitting on the eggs. They take 28 days to hatch – or at about Memorial Day.
A hen will re-nest to achieve successful hatchlings, laying eggs as late as mid-July.
Of the dozen or so eggs, four poults will make it to 16-weeks-old “in a good year,” McBride said. By the end of September or early October, the young are no longer dependent on the adults.
At that time, they will flock, the young staying with the hens, the adult males, “toms” or “gobblers,” forming their own groups.
Turkeys achieve adulthood at 2-years-old. Their life expectancy in the wild is 3 years.
The best turkey habitat in New Jersey is Cape May, Cumberland, Salem and south Gloucester counties, possibly along with parts of Atlantic County, McBride said. That is because these areas have prime habitat of rich forest and open space.
“Adults eat plenty of acorns, berries, other vegetative matter, and they can also rely on feed associated with dairy operations and backyard birdfeeders, especially in cold weather,” McBride said.
About a dozen years ago, the state basically stopped releasing turkeys.
“By then, we pretty much had turkeys in all of the available range in the state,” said McBride, who became the turkey biologist about that time.
Turkey restoration “skyrocketed” in the 1990s, because dry springs were perfect for nesting and the raccoon population was diminished by disease, Eriksen said.
“The New Jersey Division of Fish and Wildlife did a real good job,” said Eriksen, who, for the last 12 years has been the biologist in New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, and Maryland for the National Wild Turkey Federation. “It was a very aggressive program. The results are impressive. It was tremendous time and energy by the agency.”
Joe Sapia, 57-years-old, lives in the Pine Barrens around Helmetta, where his family has resided for more than 100 years. He can be reached at Snufftin@aol.com or at P.O. Box 275, Helmetta, 08828. This article was first circulated as an e-mail to friends in 2013.







































